The most powerful countries in the world in history. Empire is what form of state? The greatest empires in the world
1. British Empire (42.75 million km²)Highest peak - 1918

The British Empire is the largest state that has ever existed in the history of mankind with colonies on all inhabited continents. Largest area The empire reached in the mid-1930s, when the lands of the United Kingdom extended over 34,650,407 km² (including 8 million km² of uninhabited land), which is about 22% of the earth's land. The total population of the empire was approximately 480 million people (about one-fourth of humanity). It is the legacy of Pax Britannica that explains the role English language as the most common in the world in the fields of transport and trade.
2. Mongol Empire (38.0 million km²)
Highest flowering - 1270-1368.

Mongol Empire (Mongolian Mongolian ezent guren; Middle Mongolian ᠶᠡᠺᠡ ᠮᠣᠨᠭᠣᠯ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ, Yeke Mongγol ulus - Great Mongolian state, Mongolian Mongol ulus) - a state that emerged in the 13th century as a result of the conquests of Chinggis khan and his successors and included the most the largest contiguous territory in world history from the Danube to the Sea of Japan and from Novgorod to Southeast Asia(area approx. 38,000,000 square kilometers). Karakorum became the capital of the state.
During its heyday, it included vast territories of Central Asia, Southern Siberia, Eastern Europe, the Middle East, China and Tibet. In the second half of the 13th century, the empire began to disintegrate into uluses, headed by the Chingizids. The largest fragments of Great Mongolia were the Yuan Empire, the Ulus of Jochi (Golden Horde), the state of the Hulaguids and the Chagatai Ulus. The Great Khan Kublai, who assumed (1271) the title of Emperor Yuan and moved the capital to Khanbalyk, laid claim to supremacy over all uluses. By the beginning of the 14th century, the formal unity of the empire was restored in the form of a federation of virtually independent states.
In the last quarter of the 14th century, the Mongol Empire ceased to exist.
3. Russian Empire (22.8 million km²)
Highest flowering - 1866


The Russian Empire (Russian doref. Rossiyskaya Imperiya; also the All-Russian Empire, the Russian State or Russia) is a state that existed from October 22 (November 2), 1721 until the February Revolution and the proclamation of the republic in 1917 by the Provisional Government.
The Empire was proclaimed on October 22 (November 2, 1721) based on the results Northern War, when, at the request of the senators, the Russian Tsar Peter I the Great accepted the titles of Emperor of All Russia and Father of the Fatherland.
The capital of the Russian Empire from 1721 to 1728 and from 1730 to 1917 was St. Petersburg, and in 1728-1730 Moscow.
The Russian Empire was the third largest state ever to exist (after the British and Mongol Empires) - stretching to the Arctic Ocean in the north and the Black Sea in the south, to the Baltic Sea in the west and the Pacific Ocean in the east. The head of the empire, the All-Russian Emperor, had unlimited, absolute power until 1905.
On September 1 (14), 1917, Alexander Kerensky proclaimed the country a republic (although this issue fell within the competence of the Constituent Assembly; on January 5 (18), 1918, the Constituent Assembly also declared Russia a republic). However, the legislature of the empire - State Duma- was dissolved only on October 6 (19), 1917.
Geographical position of the Russian Empire: 35°38’17" - 77°36’40" northern latitude and 17°38'E - 169°44'W. The territory of the Russian Empire at the end of the 19th century - 21.8 million km² (that is, 1/6 of the land) - it ranked second (and third ever) in the world, after the British Empire. The article does not take into account the territory of Alaska, which was part of it from 1744 to 1867 and occupied an area of 1,717,854 km².
The regional reform of Peter I for the first time divides Russia into provinces, streamlining administration, supplying the army with provisions and recruits from the localities, and improving tax collection. Initially, the country is divided into 8 provinces headed by governors vested with judicial and administrative powers.
The provincial reform of Catherine II divides the empire into 50 provinces, divided into counties (about 500 in total). To assist governors, state and judicial chambers and other state and social institutions have been created. The governors were subordinate to the Senate. The head of the district is a police captain (elected by the district assembly of nobles).
By 1914, the empire was divided into 78 provinces, 21 regions and 2 independent districts, where 931 cities were located. Russia includes the following territories modern states: all CIS countries (without Kaliningrad region and the southern part of the Sakhalin region of the Russian Federation; Ivano-Frankivsk, Ternopil, Chernivtsi regions of Ukraine); eastern and central Poland, Estonia, Latvia, Finland, Lithuania (without the Memel region), several Turkish and Chinese regions. Some provinces and regions were united into a governorate general (Kiev, Caucasus, Siberian, Turkestan, East Siberian, Amur, Moscow). The Bukhara and Khiva khanates were official vassals, the Uriankhai region is a protectorate. For 123 years (from 1744 to 1867), the Russian Empire also owned Alaska and the Aleutian Islands, as well as part of the Pacific coast of the United States and Canada.
According to the general census of 1897, the population was 129.2 million people. The distribution of the population by territory was as follows: European Russia - 94,244.1 thousand people, Poland - 9456.1 thousand people, Caucasus - 9354.8 thousand people, Siberia - 5784.5 thousand people, Middle Asia - 7747.1 thousand people, Finland - 2555.5 thousand people.
4. Soviet Union(22.4 million km²)
Highest peak - 1945-1990.

The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, also the USSR, the Soviet Union is a state that existed from 1922 to 1991 on the territory of Eastern Europe, Northern, and parts of Central and Eastern Asia. The USSR occupied almost 1/6 of the Earth's inhabited landmass; at the time of its collapse it was the largest country in the world by area. Formed on the territory that by 1917 was occupied by the Russian Empire without Finland, part of the Polish Kingdom and some other territories.
According to the Constitution of 1977, the USSR was proclaimed a single union multinational socialist state.
After World War II, the USSR had land borders with Afghanistan, Hungary, Iran, China, North Korea (since September 9, 1948), Mongolia, Norway, Poland, Romania, Turkey, Finland, Czechoslovakia and sea borders with the USA, Sweden and Japan.
The USSR was created on December 30, 1922 by uniting the RSFSR, Ukrainian SSR, Belarusian SSR and Transcaucasian SFSR into one state association with a uniform government, capital in Moscow, executive and judicial authorities, legislative and legal systems. In 1941, the USSR entered the Second World War, and after it, along with the United States, was a superpower. The Soviet Union dominated the world socialist system and was also a permanent member of the UN Security Council.
The collapse of the USSR was characterized by an acute confrontation between representatives of the central union government and the newly elected local authorities (Supreme Councils, presidents of the union republics). In 1989-1990, the “parade of sovereignties” began. On March 17, 1991, an All-Union referendum on the preservation of the USSR was held in 9 of the 15 republics of the USSR, in which more than two-thirds of the voting citizens were in favor of preserving the renewed union. But after the August Putsch and the events that followed it, the preservation of the USSR as a state entity became virtually impossible, as stated in the Agreement on the Creation of the Commonwealth of Independent States, signed on December 8, 1991. The USSR officially ceased to exist on December 26, 1991. At the end of 1991 Russian Federation was recognized as a continuation state USSR in international legal relations and took his place on the UN Security Council.
5. Spanish Empire (20.0 million km²)
Highest flowering - 1790
The Spanish Empire (Spanish: Imperio Español) is a collection of territories and colonies that were under the direct control of Spain in Europe, America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. The Spanish Empire at the height of its power was one of largest empires in world history. Its creation is associated with the beginning of the era of great geographical discoveries, during which it became one of the first colonial empires. The Spanish Empire existed from the 15th century until (in the case of its African possessions) the end of the 20th century. The Spanish territories were united in the late 1480s with a union of Catholic kings: the King of Aragon and the Queen of Castile. Despite the fact that the monarchs continued to rule each their own lands, they foreign policy was common. In 1492 they captured Granada and completed the Reconquista in the Iberian Peninsula against the Moors. The entry of Granada into the Kingdom of Castile completed the unification of the Spanish lands, despite the fact that Spain was still divided into two kingdoms. In the same year, Christopher Columbus launched the first Spanish exploratory expedition westward across the Atlantic Ocean, discovering the New World for Europeans and establishing Spain's first overseas colonies there. From this point on, the Western Hemisphere became the main target of Spanish exploration and colonization.
In the 16th century, the Spaniards created settlements on the islands of the Caribbean, and the conquistadors destroyed such state formations as the Aztec and Inca empires on the mainland of North and South America, respectively, taking advantage of the contradictions between local peoples and using higher military technologies. Subsequent expeditions extended the empire's borders from modern Canada to the southern tip of South America, including the Falkland or Malvinas Islands. In 1519, the First Voyage around the World, begun by Ferdinand Magellan in 1519 and completed by Juan Sebastian Elcano in 1522, aimed to achieve what Columbus failed, namely the western route to Asia, and as a result included Spain in the sphere of influence Far East. Colonies were established in Guam, the Philippines and nearby islands. At the time of its Siglo de Oro, the Spanish Empire included the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Belgium, large parts of Italy, lands in Germany and France, colonies in Africa, Asia and Oceania, as well as large territories in Northern and South America. In the 17th century, Spain controlled an empire of such a scale, and its parts were so far removed from each other, which no one had achieved before.
At the end of the XVI - early XVII centuries, expeditions were undertaken in search of Terra Australis, during which a number of archipelagos and islands in the South Pacific were discovered, including the Pitcairn Islands, the Marquesas Islands, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, the Solomon Islands and New Guinea, which were declared the property of the Spanish Crown, but were not successfully colonized by it. Many of Spain's European possessions were lost after the War of the Spanish Succession in 1713, but Spain retained its overseas territories. In 1741, an important victory over Great Britain at Cartagena (modern Colombia) extended Spanish hegemony in the Americas into the 19th century. At the end of the 18th century, Spanish expeditions in the northwestern Pacific Ocean reached the coasts of Canada and Alaska, establishing a settlement on Vancouver Island and discovering several archipelagos and glaciers.
The French occupation of Spain by the troops of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1808 led to the fact that the colonies of Spain became cut off from the mother country, and the subsequent independence movement that began in 1810-1825 led to the creation of a number of new independent Spanish-American republics in South and Central America. The remnants of the four-hundred-year-old Spanish empire, including Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Spanish East Indies, continued to remain under Spanish control until the late 19th century, when most of these territories were annexed by the United States after the Spanish-American War. The remaining Pacific islands were sold to Germany in 1899.
At the beginning of the 20th century, Spain still continued to hold only territories in Africa, Spanish Guinea, Spanish Sahara and Spanish Morocco. Spain left Morocco in 1956 and granted independence to Equatorial Guinea in 1968. When Spain abandoned the Spanish Sahara in 1976, the colony was immediately annexed by Morocco and Mauritania, and then entirely by Morocco in 1980, although technically the territory remains under a UN decision. control of the Spanish administration. Today, Spain has only the Canary Islands and two enclaves on the North African coast, Ceuta and Melilla, which are administratively parts of Spain.
6. Qing Dynasty (14.7 million km²)
Highest flowering - 1790

The Great Qing State (Daicing gurun.svg Daicing Gurun, Chinese tr. 大清國, pal.: Da Qing guo) was a multinational empire created and ruled by the Manchus, which later included China. According to traditional Chinese historiography - the last dynasty of monarchical China. It was founded in 1616 by the Manchu clan of Aishin Gyoro in the territory of Manchuria, currently called northeastern China. In less than 30 years, all of China, part of Mongolia and part of Central Asia came under her rule.
The dynasty was originally called "Jin" (金 - gold), in traditional Chinese historiography "Hou Jin" (後金 - Later Jin), after the Jin Empire - the former state of the Jurchens, from which the Manchus derived themselves. In 1636 the name was changed to "Qing" (清 - "pure"). In the first half of the 18th century. the Qing government managed to establish effective management country, one of the results of which was that in this century the fastest rates of population growth were observed in China. The Qing court pursued a policy of self-isolation, which ultimately led to the fact that in the 19th century. China, part of the Qing Empire, was forcibly opened by the Western powers.
Subsequent cooperation with Western powers allowed the dynasty to avoid collapse during the Taiping Rebellion, carry out relatively successful modernization, etc. to exist until the beginning of the 20th century, but it also served as the reason for growing nationalist (anti-Manchu) sentiments.
As a result Xinhai Revolution, which began in 1911, the Qing Empire was destroyed, and the Republic of China, the national state of the Han Chinese, was proclaimed. Empress Dowager Longyu abdicated the throne on behalf of the then minor last emperor, Pu Yi, on February 12, 1912.
7. Russian kingdom (14.5 million km²)
Highest flowering - 1721

The Russian Tsardom or in the Byzantine version the Russian Tsardom is a Russian state that existed between 1547 and 1721. The name “Russian Kingdom” was the official name of Russia during this historical period. The official name was also рꙋсїѧ
In 1547, the sovereign of all Rus' and Grand Duke Moscow Ivan IV the Terrible was crowned Tsar and took the full title: “Great Sovereign, by God's grace Tsar and Grand Duke of All Rus', Vladimir, Moscow, Novgorod, Pskov, Ryazan, Tver, Yugorsk, Perm, Vyatsky, Bulgarian and others,” subsequently, with the expansion of the borders of the Russian state, “Tsar of Kazan, Tsar of Astrakhan, Tsar of Siberia” was added to the title ", "and the ruler of all the Northern countries."
In terms of title, the Russian Kingdom was preceded by the Grand Duchy of Moscow, and its successor was the Russian Empire. In historiography there is also a tradition of periodization of Russian history, according to which it is customary to talk about the emergence of a single and independent centralized Russian state during the reign of Ivan III the Great. The idea of unifying Russian lands (including those that found themselves after the Mongol invasion as part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Poland) and restoring the Old Russian state could be traced throughout the existence of the Russian state and was inherited by the Russian Empire.
8. Yuan Dynasty (14.0 million km²)
Highest flowering - 1310

Empire (in the Chinese tradition - dynasty) Yuan (Ikh Yuan ul.PNG Mong. Ikh Yuan Uls, Great Yuan State, Dai Ön Yeke Mongghul Ulus.PNG Dai Ön Yeke Mongghul Ulus; Chinese example: 元朝, pinyin: Yuáncháo; Vietnamese. Nhà Nguyên (Nguyên triều), House (Dynasty) of Nguyen) was a Mongol state whose main territory was China (1271-1368). Founded by Genghis Khan's grandson, the Mongol Khan Kublai Khan, who completed his conquest of China in 1279. The dynasty fell as a result of the Red Turban Rebellion of 1351-68. Official Chinese history This dynasty was recorded during the subsequent Ming Dynasty and is called "Yuan Shi".
9. Umayyad Caliphate (13.0 million km²)
Highest flowering - 720-750.

Omayydy (arab. الأمويوild) or Banu Umay (arab. Lf. أĕuction) - the Khalifov dynasty, founded by Muavia in 661. Omeyayads of the Sufyanid and Marvanid branches ruled in the Damascus Caliphate until the middle of the VIII century. In 750, as a result of the uprising of Abu Muslim, their dynasty was overthrown by the Abbasids, and all the Umayyads were destroyed, except for the grandson of the caliph Hisham Abd al-Rahman, who founded the dynasty in Spain (Cordoba Caliphate). The ancestor of the dynasty was Omayya ibn Abdshams, son of Abdshams ibn Abdmanaf and cousin Abdulmuttalib. Abdshams and Hashim were twin brothers.
10. Second French colonial empire (13.0 million km²)
Highest peak - 1938

Evolution of the French Colonial Empire (year is indicated in the upper left corner):

The French colonial empire (French L’Empire colonial français) is the totality of the colonial possessions of France in the period between 1546-1962. Like the British Empire, France had colonial territories in all regions of the world, but its colonial policies differed significantly from Britain's. The remnants of the once vast colonial empire are the modern overseas departments of France (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, etc.) and a special territory sui generis (the island of New Caledonia). The modern legacy of the French colonial era is also the union of French-speaking countries (Francophonie).
6,460 views
The continuous struggle for territorial dominance, possession of resources and endless wars are the basis of human history. Seizing the lands of nearby peoples and entire countries, huge empires appeared in different parts.
But great empires, which liked to call themselves “Eternals,” appeared on the world map and safely disappeared from it after different times. However, some of the huge empires left behind traces that are felt in politics and the lives of ordinary people to this day.
The greatest empires in human history
Persian Empire (Achaemenid Empire, 550 – 330 BC)

Cyrus II is considered the founder of the Persian Empire. He began his conquests in 550 BC. e. with the subjugation of Media, after which Armenia, Parthia, Cappadocia and the Lydian kingdom were conquered. Did not become an obstacle to the expansion of the empire of Cyrus and Babylon, whose powerful walls fell in 539 BC. e.
While conquering neighboring territories, the Persians tried not to destroy the conquered cities, but, if possible, to preserve them. Cyrus restored captured Jerusalem, like many Phoenician cities, facilitating the return of Jews from Babylonian captivity.
The Persian Empire under Cyrus extended its possessions from Central Asia to the Aegean Sea. Only Egypt remained unconquered. The country of the pharaohs submitted to the heir of Cyrus, Cambyses II. However, the empire reached its peak under Darius I, who switched from conquests to domestic policy. In particular, the king divided the empire into 20 satrapies, which completely coincided with the territories of the captured states.
In 330 BC. e. The weakening Persian Empire fell under the onslaught of the troops of Alexander the Great.
Roman Empire (27 BC – 476)

Ancient Rome was the first state in which the ruler received the title of emperor. Beginning with Octavian Augustus, the 500-year history of the Roman Empire had a direct impact on European civilization and also left a cultural mark on the countries of North Africa and the Middle East.
The uniqueness of Ancient Rome is that it was the only state whose possessions included the entire Mediterranean coast.
At the height of the Roman Empire, its territories extended from the British Isles to the Persian Gulf. According to historians, by 117 the population of the empire reached 88 million people, which was approximately 25% of the total number of inhabitants of the planet.
Architecture, construction, art, law, economics, military affairs, the principles of government of Ancient Rome - this is what the foundation of the entire European civilization. It was in imperial Rome that Christianity assumed the status of state religion and began its spread throughout the world.
Byzantine Empire (395 – 1453)

The Byzantine Empire has no equal in the length of its history. Originating at the end of antiquity, it existed until the end European Middle Ages. For more than a thousand years, Byzantium was a kind of connecting link between the civilizations of the East and West, influencing both the states of Europe and Asia Minor.
But if Western European and Middle Eastern countries inherited the rich material culture of Byzantium, then Old Russian state turned out to be the successor to her spirituality. Constantinople fell, but the Orthodox world found its new capital in Moscow.
Located at the crossroads of trade routes, rich Byzantium was a coveted land for neighboring states. Having reached its maximum borders in the first centuries after the collapse of the Roman Empire, then it was forced to defend its possessions. In 1453, Byzantium could not resist a more powerful enemy - the Ottoman Empire. With the capture of Constantinople, the road to Europe was open for the Turks.
Arab Caliphate (632-1258)

As a result of Muslim conquests in the 7th–9th centuries, the theocratic Islamic state of the Arab Caliphate arose in the entire Middle Eastern region, as well as in certain regions of Transcaucasia, Central Asia, North Africa and Spain. The period of the Caliphate went down in history as the “Golden Age of Islam”, as the time of the highest flowering of Islamic science and culture.
One of the caliphs of the Arab state, Umar I, purposefully secured the character of a militant church for the Caliphate, encouraging religious zeal in his subordinates and prohibiting them from owning land property in the conquered countries. Umar motivated this by the fact that “the interests of the landowner attract him more to peaceful activities than to war.”
In 1036, the invasion of the Seljuk Turks was disastrous for the Caliphate, but the defeat of the Islamic state was completed by the Mongols.
Caliph An-Nasir, wanting to expand his possessions, turned to Genghis Khan for help, and unknowingly opened the way for the destruction of the Muslim East by the Mongol horde of thousands.
Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)

The Holy Roman Empire is an interstate entity that existed in Europe from 962 to 1806. The core of the empire was Germany, which was joined by the Czech Republic, Italy, the Netherlands, as well as some regions of France during the period of the highest prosperity of the state.
Almost the entire period of the empire's existence, its structure had the character of a theocratic feudal state, in which the emperors laid claim to supreme power in the Christian world. However, the struggle with the papal throne and the desire to possess Italy significantly weakened the central power of the empire.
In the 17th century, Austria and Prussia moved to leading positions in the Holy Roman Empire. But very soon the antagonism of two influential members of the empire, which resulted in a policy of conquest, threatened their integrity common house. The end of the empire in 1806 was marked by the strengthening France led by Napoleon.
Ottoman Empire (1299–1922)

In 1299, Osman I created a Turkic state in the Middle East, which was destined to exist for more than 600 years and radically influence the fate of the countries of the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the date when the Ottoman Empire finally gained a foothold in Europe.
Period of greatest power Ottoman Empire falls on the 16th-17th centuries, but the state achieved its greatest conquests under Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent.
The borders of the empire of Suleiman I extended from Eritrea in the south to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the north, from Algeria in the west to the Caspian Sea in the east.
The period from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 20th century was marked by bloody military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and Russia. Territorial disputes between the two states mainly revolved around Crimea and Transcaucasia. The First put an end to them world war, as a result of which the Ottoman Empire, divided between the Entente countries, ceased to exist.
Russian Empire (1721–1917, until 1991 - in the form of the USSR, and to this day in the form of the Russian Federation)

The history of the Russian Empire dates back to October 22, 1721, after Peter I accepted the title of All-Russian Emperor. From that time until 1905, the monarch who became the head of the state was endowed with absolute power.
In terms of area, the Russian Empire was second only to the Mongol and British empires - 21,799,825 square meters. km, and was the second (after British) in terms of population - about 178 million people.
Constant expansion of territory – characteristic feature Russian Empire. But if the advance to the east was mostly peaceful, then in the west and south Russia had to prove its territorial claims through numerous wars - with Sweden, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, Persia, and the British Empire.
The growth of the Russian Empire has always been viewed with particular caution by the West. The negative perception of Russia was facilitated by the appearance of the so-called “Testament of Peter the Great,” a document fabricated in 1812 by French political circles. “The Russian state must establish power over all of Europe” is one of the key phrases of the Testament, which will haunt the minds of Europeans for a long time.
Mongol Empire (1206–1368)

The Mongol Empire is the largest state formation in history by territory.
During the period of its power, towards the end of the 13th century, the empire extended from the Sea of Japan to the banks of the Danube. The total area of the Mongols' possessions reached 38 million square meters. km.
Given the enormous size of the empire, managing it from the capital, Karakorum, was almost impossible. It is no coincidence that after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227, the process of gradual division of the conquered territories into separate uluses began, the most significant of which became the Golden Horde.
The economic policy of the Mongols in the occupied lands was primitive: its essence boiled down to the imposition of tribute on the conquered peoples. Everything collected went to support the needs of a huge army, according to some sources, reaching half a million people. The Mongol cavalry was the most deadly weapon of the Genghisids, which not many armies could resist.
Inter-dynastic strife destroyed the empire - it was they who stopped the expansion of the Mongols to the West. This was soon followed by the loss of the conquered territories and the capture of Karakorum by Ming dynasty troops.
British Empire (1497–1949)

The British Empire is the largest colonial power both in terms of territory and population.
The empire reached its greatest scale by the 30s of the 20th century: the land area of the United Kingdom, including its colonies, totaled 34 million 650 thousand square meters. km., which accounted for approximately 22% of the earth's land. Total number The population of the empire reached 480 million people - every fourth inhabitant of the Earth was a subject of the British Crown.
Many factors contributed to the success of British colonial policy: strong army and navy, developed industry, the art of diplomacy. The expansion of the empire significantly influenced global geopolitics. First of all, this is the spread of British technology, trade, language, and forms of government throughout the world.
Colored history
Pain and fear: 10 main corporal punishments in Rus'...
The history of mankind is a continuous struggle for territorial dominance. Great empires either appeared on the political map of the world or disappeared from it. Some of them were destined to leave an indelible mark behind them.
Persian Empire (Achaemenid Empire, 550 – 330 BC)
Cyrus II is considered the founder of the Persian Empire. He began his conquests in 550 BC. e. with the subjugation of Media, after which Armenia, Parthia, Cappadocia and the Lydian kingdom were conquered. Did not become an obstacle to the expansion of the empire of Cyrus and Babylon, whose powerful walls fell in 539 BC. e.
While conquering neighboring territories, the Persians tried not to destroy the conquered cities, but, if possible, to preserve them. Cyrus restored captured Jerusalem, like many Phoenician cities, facilitating the return of Jews from Babylonian captivity.
The Persian Empire under Cyrus extended its possessions from Central Asia to the Aegean Sea. Only Egypt remained unconquered. The country of the pharaohs submitted to the heir of Cyrus, Cambyses II. However, the empire reached its heyday under Darius I, who switched from conquests to internal politics. In particular, the king divided the empire into 20 satrapies, which completely coincided with the territories of the captured states.
In 330 BC. e. The weakening Persian Empire fell under the onslaught of the troops of Alexander the Great.
Roman Empire (27 BC – 476)

Ancient Rome was the first state in which the ruler received the title of emperor. Beginning with Octavian Augustus, the 500-year history of the Roman Empire had a direct impact on European civilization and also left a cultural mark on the countries of North Africa and the Middle East.
The uniqueness of Ancient Rome is that it was the only state whose possessions included the entire Mediterranean coast.
At the height of the Roman Empire, its territories extended from the British Isles to the Persian Gulf. According to historians, by 117 the population of the empire reached 88 million people, which was approximately 25% of the total number of inhabitants of the planet.
Architecture, construction, art, law, economics, military affairs, the principles of government of Ancient Rome - this is what the foundation of the entire European civilization is based on. It was in imperial Rome that Christianity assumed the status of state religion and began its spread throughout the world.
Byzantine Empire (395 – 1453)

The Byzantine Empire has no equal in the length of its history. Originating at the end of antiquity, it existed until the end of the European Middle Ages. For more than a thousand years, Byzantium was a kind of connecting link between the civilizations of the East and West, influencing both the states of Europe and Asia Minor.
But if Western European and Middle Eastern countries inherited the rich material culture of Byzantium, then the Old Russian state turned out to be the successor to its spirituality. Constantinople fell, but the Orthodox world found its new capital in Moscow.
Located at the crossroads of trade routes, rich Byzantium was a coveted land for neighboring states. Having reached its maximum borders in the first centuries after the collapse of the Roman Empire, then it was forced to defend its possessions. In 1453, Byzantium could not resist a more powerful enemy - the Ottoman Empire. With the capture of Constantinople, the road to Europe was open for the Turks.
Arab Caliphate (632-1258)

As a result of Muslim conquests in the 7th–9th centuries, the theocratic Islamic state of the Arab Caliphate arose in the entire Middle Eastern region, as well as in certain regions of Transcaucasia, Central Asia, North Africa and Spain. The period of the Caliphate went down in history as the “Golden Age of Islam”, as the time of the highest flowering of Islamic science and culture.
One of the caliphs of the Arab state, Umar I, purposefully secured the character of a militant church for the Caliphate, encouraging religious zeal in his subordinates and prohibiting them from owning land property in the conquered countries. Umar motivated this by the fact that “the interests of the landowner attract him more to peaceful activities than to war.”
In 1036, the invasion of the Seljuk Turks was disastrous for the Caliphate, but the defeat of the Islamic state was completed by the Mongols.
Caliph An-Nasir, wanting to expand his possessions, turned to Genghis Khan for help, and unknowingly opened the way for the destruction of the Muslim East by the Mongol horde of thousands.
Mongol Empire (1206–1368)

The Mongol Empire is the largest state formation in history by territory.
During the period of its power, towards the end of the 13th century, the empire extended from the Sea of Japan to the banks of the Danube. The total area of the Mongols' possessions reached 38 million square meters. km.
Given the enormous size of the empire, managing it from the capital, Karakorum, was almost impossible. It is no coincidence that after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227, the process of gradual division of the conquered territories into separate uluses began, the most significant of which became the Golden Horde.
The economic policy of the Mongols in the occupied lands was primitive: its essence boiled down to the imposition of tribute on the conquered peoples. Everything collected went to support the needs of a huge army, according to some sources, reaching half a million people. The Mongol cavalry was the most deadly weapon of the Genghisids, which not many armies could resist.
Inter-dynastic strife destroyed the empire - it was they who stopped the expansion of the Mongols to the West. This was soon followed by the loss of the conquered territories and the capture of Karakorum by Ming dynasty troops.
Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
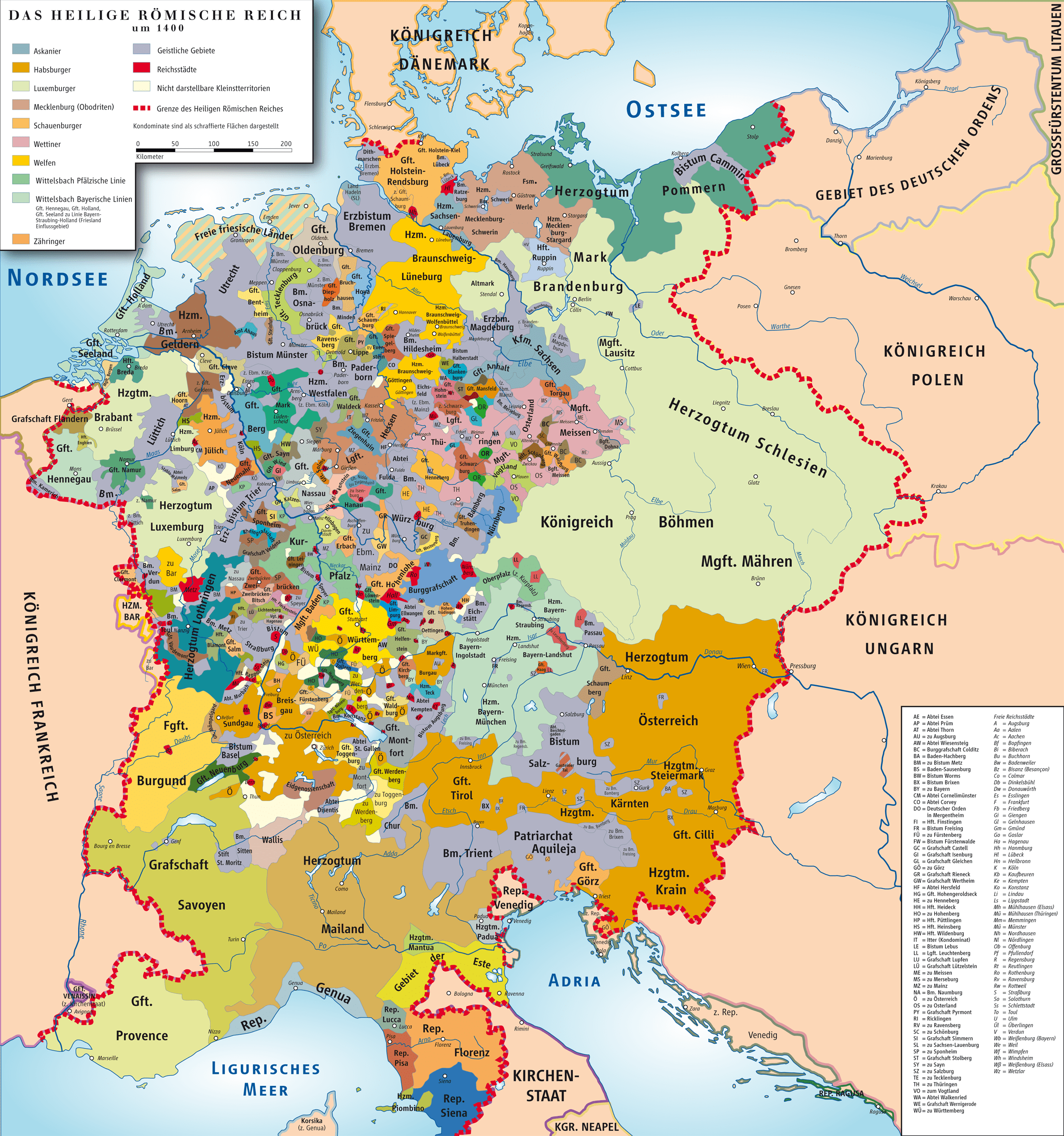
The Holy Roman Empire is an interstate entity that existed in Europe from 962 to 1806. The core of the empire was Germany, which was joined by the Czech Republic, Italy, the Netherlands, as well as some regions of France during the period of the highest prosperity of the state.
Almost the entire period of the empire's existence, its structure had the character of a theocratic feudal state, in which the emperors laid claim to supreme power in the Christian world. However, the struggle with the papal throne and the desire to possess Italy significantly weakened the central power of the empire.
In the 17th century, Austria and Prussia moved to leading positions in the Holy Roman Empire. But very soon the antagonism of two influential members of the empire, which resulted in a policy of conquest, threatened the integrity of their common home. The end of the empire in 1806 was marked by the strengthening France led by Napoleon.
Ottoman Empire (1299–1922)

In 1299, Osman I created a Turkic state in the Middle East, which was destined to exist for more than 600 years and radically influence the fate of the countries of the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the date when the Ottoman Empire finally gained a foothold in Europe.
The period of the greatest power of the Ottoman Empire occurred in the 16th-17th centuries, but the state achieved its greatest conquests under Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent.
The borders of the empire of Suleiman I extended from Eritrea in the south to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the north, from Algeria in the west to the Caspian Sea in the east.
The period from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 20th century was marked by bloody military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and Russia. Territorial disputes between the two states mainly revolved around Crimea and Transcaucasia. They were put to an end by the First World War, as a result of which the Ottoman Empire, divided between the Entente countries, ceased to exist.
British Empire (1497–1949)

The British Empire is the largest colonial power both in terms of territory and population.
The empire reached its greatest scale by the 30s of the 20th century: the land area of the United Kingdom, including its colonies, totaled 34 million 650 thousand square meters. km., which accounted for approximately 22% of the earth's land. The total population of the empire reached 480 million people - every fourth inhabitant of the Earth was a subject of the British Crown.
The success of British colonial policy was facilitated by many factors: a strong army and navy, developed industry, and the art of diplomacy. The expansion of the empire significantly influenced global geopolitics. First of all, this is the spread of British technology, trade, language, and forms of government throughout the world.
The decolonization of Britain occurred after the end of the Second World War. Although the country was among the victorious states, it found itself on the verge of bankruptcy. It was only thanks to an American loan of $3.5 billion that Great Britain was able to overcome the crisis, but at the same time lost world dominance and all its colonies.
Russian Empire (1721–1917)

The history of the Russian Empire dates back to October 22, 1721, after Peter I accepted the title of All-Russian Emperor. From that time until 1905, the monarch who became the head of the state was endowed with absolute power.
In terms of area, the Russian Empire was second only to the Mongol and British empires - 21,799,825 square meters. km, and was the second (after British) in terms of population - about 178 million people.
Constant expansion of territory is a characteristic feature of the Russian Empire. But if the advance to the east was mostly peaceful, then in the west and south Russia had to prove its territorial claims through numerous wars - with Sweden, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, Persia, and the British Empire.
The growth of the Russian Empire has always been viewed with particular caution by the West. The negative perception of Russia was facilitated by the appearance of the so-called “Testament of Peter the Great,” a document fabricated in 1812 by French political circles. “The Russian state must establish power over all of Europe” is one of the key phrases of the Testament, which will haunt the minds of Europeans for a long time.
In our world, nothing lasts forever: after birth and blossoming, decline inevitably follows. This rule also applies to states. Over the thousands of years of history, hundreds of states have been created and collapsed. Let's find out which of them existed on Earth the longest, until they disintegrated for one reason or another. Perhaps some of them did not amaze the world with their grandeur and brilliance, but they were strong with their centuries-old history.
Portuguese Colonial Empire
560 years (1415 -1975)
The prerequisites for the creation of the Portuguese Colonial Empire appeared simultaneously with the beginning of the Great Geographical Discoveries. By 1415, Portuguese sailors, of course, had not yet reached the shores of America, but were already actively exploring the African continent, beginning the search for a short sea route to India. The Portuguese declared the open lands their property, erecting forts and fortresses everywhere.
At its height, the Portuguese Colonial Empire had fortifications in West Africa, East and South Asia, India and the Americas. The Portuguese Empire became the first state in history to unite territories on four continents under its flag. Thanks to the trade in spices and jewelry, the Portuguese treasury was bursting with gold and silver, which allowed the state to exist for such a long time.

The Napoleonic wars, internal contradictions and external enemies nevertheless undermined the power of the state, and by the beginning of the 20th century there was no trace left of the former greatness of the Portuguese Colonial Empire. The empire officially ceased to exist in 1975, when democracy was established in the metropolis.
624 years (1299 AD -1923 AD)
The state, founded by Turkic tribes in 1299, reached its peak in the 17th century. The huge multinational Ottoman Empire stretched from the borders of Austria to the Caspian Sea, owning territories in Europe, Africa, and Asia. Wars with the Russian Empire, loss in the First World War, internal contradictions and constant Christian uprisings undermined the strength of the Ottoman Empire. In 1923, the monarchy was abolished, and in its place the Republic of Turkey was created.
Khmer Empire
629 years (802 AD -1431 AD)
Not every person has heard of the existence of the Khmer Empire, which is one of the oldest government entities in history. The Khmer Empire was formed as a result of the unification of the Khmer tribes who lived in the 8th century AD. on the territory of Indochina. At the time of its greatest power, the Khmer Empire included the territories of Cambodia, Thailand, Vietnam and Laos. But its rulers did not calculate the gigantic costs of building temples and palaces, which gradually depleted the treasury. The weakened state in the first half of the 15th century was finally finished off by the invasion of the Thai tribes.
Kanem
676 years (700 AD -1376 AD)
Despite the fact that individual African tribes do not pose a threat, when united, they can create a strong and warlike state. This is exactly how the Kanem Empire was formed, located for almost 700 years in the territory of modern Libya, Nigeria and Chad.
 Kanema Territory | commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kanem-Bornu.svg
Kanema Territory | commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kanem-Bornu.svg The cause of the fall of a strong empire was internal strife after the death of the last emperor, who had no heirs. Taking advantage of this, various tribes located on the borders invaded the empire from different sides, hastening its fall. The surviving indigenous people were forced to leave the cities and return to a nomadic lifestyle.
Holy Roman Empire
844 years (962 AD – 1806 AD)

The Holy Roman Empire is not the same Roman Empire, whose iron legions captured almost the entire world known to ancient Europe. The Holy Roman Empire was not even located in Italy, but on the territory of modern Germany, Austria, Holland, the Czech Republic and part of Italy. The unification of the lands took place in 962, and the new Empire was intended to become a continuation of the Western Roman Empire. European order and discipline allowed this state to exist for eight and a half centuries, until complex system public administration, having degraded, weakened the central power, which led to the decline and collapse of the Holy Roman Empire.
Kingdom of Silla
992 years (57 BC – 935 AD)

At the end of the first century BC. on the Korean Peninsula, three kingdoms desperately fought for a place in the sun, one of which - Silla - managed to defeat its enemies, annexed their lands and founded a powerful dynasty that lasted almost a thousand years, which ingloriously disappeared in the fires civil war.
994 years (980 AD -1974 AD)

We often think that before the arrival of European colonialists, Africa was a completely wild area inhabited by primitive tribes. But on African continent there was a place for an empire that existed for almost a thousand years! Founded in 802 by united Ethiopian tribes, the empire did not last 6 years before its millennium, collapsing as a result of a coup d'etat.
1100 years (697 AD - 1797 AD)

The Most Serene Republic of Venice with its capital Venice was founded in 697 thanks to the forced unification of communities against the troops of the Lombards - Germanic tribes that settled in the upper reaches of Italy during the Great Migration. Extremely successful geographical location at the intersection of most trade routes, they immediately made the Republic one of the richest and most influential states in Europe. However, the discovery of America and the sea route to India was the beginning of the end for this state. The volume of goods entering Europe through Venice decreased - traders began to prefer more convenient and safe sea routes. The Venetian Republic finally ceased to exist in 1797, when Napoleon Bonaparte's troops occupied Venice without resistance.
Papal States
1118 years (752 AD – 1870 AD)
 Papal States | Wikipedia
Papal States | Wikipedia After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the influence of Christianity in Europe grew increasingly stronger: influential people adopted Christianity, entire lands were given to churches, and donations were made. The day was not far off when the Catholic Church would gain political power in Europe: this happened in 752, when the Frankish king Pepin the Short gave the pope a large region in the center of the Apennine Peninsula. Since then, the power of the popes has fluctuated depending on the place of religion in European society: from absolute power in the Middle Ages, to a gradual loss of influence closer to the 18th and 19th centuries. In 1870, the lands of the Papal States came under the control of Italy, and only the Vatican City, the city-state in Rome, remained for the Catholic Church.
Kingdom of Kush
about 1200 years (9th century BC – 350 AD)
The Kingdom of Kush has always been in the shadow of another state - Egypt, which has always attracted the attention of historians and chroniclers. Located in the northern part of modern Sudan, the state of Kush posed a serious danger to its neighbors, and during its heyday it controlled almost the entire territory of Egypt. We do not know the detailed history of the kingdom of Kush, but the chronicles note that in 350 Kush was conquered by the kingdom of Aksum.
Roman Empire
1480 years (27 BC – 1453 AD)
Rome is an eternal place on seven hills! At least, that’s what the inhabitants of the Western Roman Empire thought: it seemed that the eternal city would never fall to the onslaught of enemies. But times have changed: 500 years after the civil war and the founding of the empire, Rome was conquered by invading Germanic tribes, marking the fall of the western part of the empire. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, often called Byzantium, continued to exist until 1453, when Constantinople fell to the Turks.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.





